In this part of the Qt4 tutorial, we will introduce the Qt4 library.
We will install the Qt4 library and create our first small Qt4 application.
The last step is installing, or moving files to the directories.
The last thing that we do, is adding the qt4 path to the PATH system variable. The bash users, need to edit the either the .profile file or the .bashrc file.
This chapter was an introduction to the Qt4 library.
Qt Development Frameworks
Qt toolkit was initially developed by Trolltech, a Norwegian software company. In 2008 the company was acquired by Nokia. The company was renamed to Qt Development Frameworks. In August 2012 a Finnish development company Digia acquired Qt software technologies from Nokia. Meanwhile a Qt Project was created in which the development of open source Qt continues. The website for the open source Qt toolkit can be found at qt-project.org.Qt toolkit
Qt is a cross-platform application development framework. Some of the well known applications developed with Qt are KDE, Opera, Google Earth, Skype, VLC, Maya or Mathematica. Qt was first publicly released on May 1995. It is dual licensed. It can be used for creating open source applications as well as commercial ones. Qt toolkit is a very powerful toolkit. It is well established in the open source community. Thousands of open source developers use Qt all over the world.Download
We go to the download page. We can have either an online or offline installation. It is possible to choose to download the whole Qt4 SDK or get the parts of the SDK separatly. The complete SDK has some additional development tools. These can be also downloaded later. In this page we will show how to install Qt libraries 4.8.3 for Linux.$ ls qt-everywhere-opensource-src-4.8.3.tar.gz qt-everywhere-opensource-src-4.8.3.tar.gzFrom the download page we download the Qt4 libraries.
$ tar -xzvf qt-everywhere-opensource-src-4.8.3.tar.gzThe command will decompress all the files to a directory qt-everywhere-opensource-src-4.8.3.
$ du -hs qt-everywhere-opensource-src-4.8.3 685M qt-everywhere-opensource-src-4.8.3The size of the directory is now 685 MB.
$ cd qt-everywhere-opensource-src-4.8.3/We go to the created directory. Now it is time to carefully read the README and the INSTALL file. There we will find detailed installation instructions. The installation is easy and straightforward.
Install
We install the library the classic way. On Unix systems, installation of a software is divided into three steps.- Configuration
- Building
- Installation
$ ./configure -prefix /usr/local/qt4 Which edition of Qt do you want to use ? Type 'c' if you want to use the Commercial Edition. Type 'o' if you want to use the Open Source Edition.First we run the configure script. The script will ask whether we want the commercial or open source edition of the Qt4 library. The script will configure the library for our machine type. By default, the qt will be installed in /usr/local/Trolltech/Qt-4.8.3 directory. This can be changed by the -prefix parameter of the configure script. We install the library into the /usr/local/qt4 directory. Note that the installation word has two meanings here. It is the whole process consisting of all three steps. And it also means 'moving files to specific directories', which is the last, third step.
This is the Open Source Edition. You are licensed to use this software under the terms of the Lesser GNU General Public License (LGPL) versions 2.1. You are also licensed to use this software under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL) versions 3. Type '3' to view the GNU General Public License version 3. Type 'L' to view the Lesser GNU General Public License version 2.1. Type 'yes' to accept this license offer. Type 'no' to decline this license offer. Do you accept the terms of either license? yesConfirming licence agreement.
Qt is now configured for building. Just run 'make'. Once everything is built, you must run 'make install'. Qt will be installed into /usr/local/qt4 To reconfigure, run 'make confclean' and 'configure'.We get this message after the configure script finishes.
$ makeWe use the
make command to start the build process.
The building of the Qt toolkit can take several hours. It depends on the
power of your processor.
The last step is installing, or moving files to the directories.
sudo make installThis command finishes the installation process. The library is now installed in /usr/local/qt4 directory.
$ du -sh /usr/local/qt4 435M /usr/local/qt4The size of the directory is 435 MB. As we can see, Qt is a huge library.
The last thing that we do, is adding the qt4 path to the PATH system variable. The bash users, need to edit the either the .profile file or the .bashrc file.
PATH=/usr/local/qt4/bin:$PATH export PATHWe have added a path to the bin directory of the Qt4 library to the PATH environment variable. The changes will be active after another login.
Testing a small example
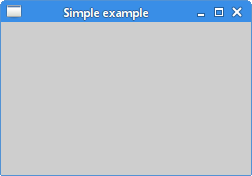
Finally we will write a small code example.#include <QApplication>
#include <QWidget>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
QWidget window;
window.resize(250, 150);
window.setWindowTitle("Simple example");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
To build this example, we will use a very handy tool called qmake.
qmake -project qmake makeIf the qt4 installation directory is not a part of the PATH variable, we can provide the full path to the qmake tool.
/usr/local/qt4/bin/qmake -project /usr/local/qt4/bin/qmake make

Figure: Simple example
Installation finished OK.
This chapter was an introduction to the Qt4 library.
No comments:
Post a Comment